报告人:Thomas Algeo, University of Cincinnati, CUG-Wuhan, CDUT
报告时间:2025年5月21日(星期三)下午14 : 30
报告地点:西康路1号河海大学海洋学院507会议室
主持人:刘犟嗣 讲师
报告人简介:

Thomas Algeo completed his Ph.D. at the University of Michigan in 1989 and worked in the oil patch for several years before joining the faculty of the University of Cincinnati in 1991. He has specialized in the development of elemental proxies for paleoenvironmental analysis, laying the foundation for the modern approach to reconstruction of redox, salinity, and productivity conditions in paleoenvironmental systems. He has studied all of the Big Five mass extinctions and is the author of a leading theory for the Late Devonian extinctions, linking them to the evolution of vascular land plants.
报告摘要:
Salinity has been a challenging feature of paleodepositional systems to reconstruct. Recent work by Prof. Algeo and his colleagues has demonstrated the robustness of multiple elemental proxies for estimation of watermass salinity in ancient shale/mudstone formations. This talk will review recent work in reconstruction of salinity in epicratonic and continental-margin aqueous systems from Mesozoic to Paleoproterozoic in age, with examples drawn from many regions including the Nanhua Basin of South China. Some of the important findings of this work are that (1) around half of the dozens of epicratonic shale formations examined to date were deposited under brackish or (more rarely) freshwater conditions, rather than fully marine conditions as previously assumed; (2) salinity variation generally correlates strongly with variation in redox and productivity conditions; and (3) the expression in cratonic systems of many geologic events (e.g., the Toarcian OAE) was influenced by salinity fluctuations.
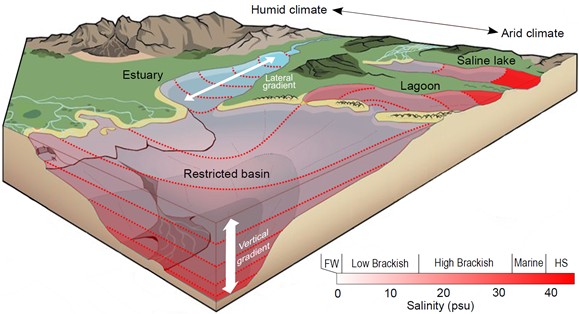
Figure: Spectrum of salinity facies that can be identified using elemental salinity proxies. Image from Algeo et al. (2025), News and Views: Are elemental salinity proxies worth their salt? Journal of Earth Sciences.



